Contents
Introduction to Thawing Pipes Naturally
Frozen pipes pose a significant challenge during cold weather, potentially leading to disruptions in water supply, costly repairs, and even property damage. Understanding the dynamics of frozen pipes and the natural thawing process is crucial for homeowners and property managers facing this common winter dilemma. In this detailed exploration, we delve into the complexities of how pipes freeze and, more importantly, the mechanisms and considerations involved in their natural thawing.
Frozen pipes occur when water within the plumbing system solidifies due to exposure to subzero temperatures, creating blockages that hinder water flow. This phenomenon is not merely an inconvenience; it represents a potential hazard that demands attention and informed action. Through this comprehensive guide, we aim to empower readers with the knowledge and strategies needed to effectively address frozen pipes and facilitate their natural thawing.
The process of thawing frozen pipes naturally is influenced by a myriad of factors, including the thickness and material of the pipes, the severity of freezing, ambient temperature, and proximity to heat sources or insulation. By unraveling these variables, we can gain insight into the dynamics of the thawing process and develop effective strategies for its facilitation.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the intricate interplay of these factors, shedding light on the physics behind the natural thawing process. From the gradual infiltration of heat into frozen pipes to the molecular changes that occur as water transitions from a solid to a liquid state, we will uncover the mechanisms that drive the thawing journey.
Furthermore, we will examine practical considerations such as the timeframe for natural thawing, methods for enhancing the thawing process, safety precautions, and preventative measures for future freezing incidents. By arming ourselves with this knowledge, we can navigate the challenges of frozen pipes with confidence and resilience.
Ultimately, our goal is not only to provide a comprehensive understanding of frozen pipes and their thawing process but also to empower readers to take proactive measures to protect their plumbing infrastructure and mitigate the risks associated with freezing temperatures. Through education, preparedness, and informed action, we can ensure that frozen pipes become a manageable challenge rather than a daunting obstacle.
Factors Affecting Thawing Time
In the journey of thawing pipes naturally, various factors come into play, influencing the duration and effectiveness of the thawing process. Understanding these factors is crucial for devising effective thawing strategies and managing expectations regarding thawing timeframes. Here, we delve into the intricate variables that shape the thawing journey:
Thickness and Material of Pipes:
The thickness and material composition of pipes significantly impact their ability to conduct heat and, consequently, the rate at which they thaw. Thicker pipes tend to retain cold temperatures longer and may require more time to thaw compared to thinner pipes. Additionally, certain materials, such as metal or PVC, conduct heat differently, affecting the overall thawing process.
Severity of Freezing:
The severity of freezing, ranging from partial blockages to complete ice formation, directly influences the time required for pipes to thaw naturally. Partial blockages may thaw relatively quickly, allowing water to flow again within a short timeframe. However, complete ice blockages may require more time and effort to fully thaw, especially if the ice formation extends over a significant length of the pipe.
Ambient Temperature and Weather Conditions:
The ambient temperature surrounding the frozen pipes plays a critical role in the thawing process. Warmer temperatures facilitate the transfer of heat to the frozen pipes, accelerating the thawing process. Conversely, colder temperatures may impede thawing progress, prolonging the time required for pipes to thaw naturally. Weather conditions, such as wind chill and humidity, also affect heat transfer and, consequently, the thawing rate.
Proximity to Heat Sources or Insulation:
The proximity of frozen pipes to heat sources or insulation significantly impacts the thawing time. Pipes located closer to heat sources, such as heating vents or radiators, may thaw more quickly due to direct heat exposure. Similarly, pipes insulated with materials like foam or fiberglass retain heat better and may thaw more efficiently compared to uninsulated pipes.
By understanding and carefully considering these factors, homeowners and property managers can develop effective thawing strategies tailored to their specific circumstances. In the subsequent sections, we will explore the natural thawing process in greater detail, providing insights into the mechanisms and considerations involved in facilitating the gradual return of water flow within frozen pipes.
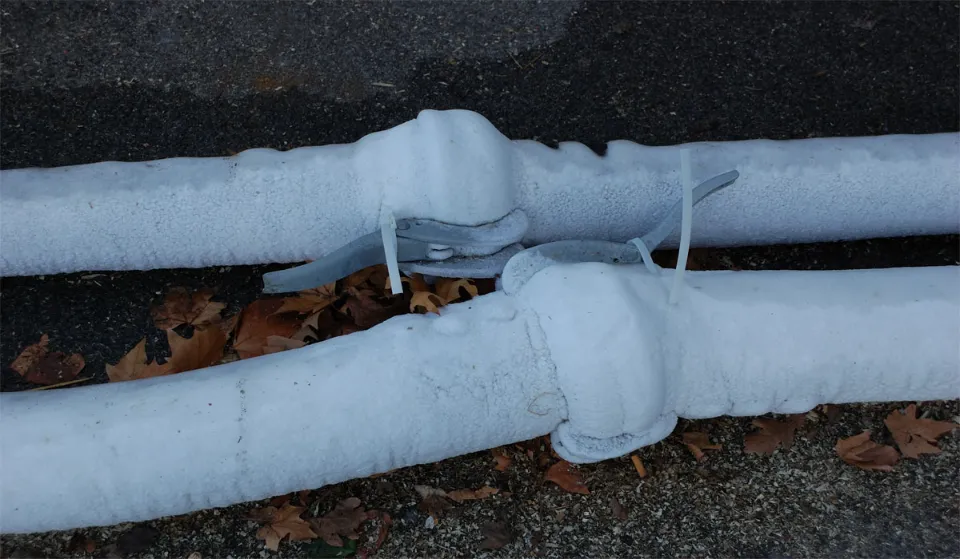

Natural Thawing Process
Understanding the natural thawing process is essential for effectively managing frozen pipes and facilitating their gradual return to functionality. In this section, we delve into the intricate dynamics of how heat interacts with frozen pipes, driving the transition from a solid to a liquid state. Here are the key elements of the natural thawing process.
Description of Heat Transfer in Frozen Pipes:
Heat transfer plays a central role in the thawing of frozen pipes. When heat is applied to the exterior of a frozen pipe, it gradually penetrates through the pipe wall, transferring thermal energy to the ice within. This heat transfer process occurs through conduction, where molecules in the pipe material vibrate and transfer energy to adjacent molecules, eventually reaching the ice and raising its temperature.
Molecular Changes During Thawing:
As heat is absorbed by the ice within the pipe, molecular bonds holding the water molecules in a crystalline structure begin to weaken. This weakening of bonds allows the water molecules to break free from their frozen state and transition into a liquid state. As the ice melts, water begins to flow within the pipe, gradually restoring water flow and functionality.
Mechanisms Involved in the Natural Thawing Process:
The natural thawing process relies on the gradual transfer of heat to the frozen pipe, allowing for controlled and uniform thawing. As heat penetrates the pipe, it warms the ice from the outside in, ensuring that the entire ice blockage gradually reaches its melting point. This gradual thawing process helps prevent rapid temperature changes and potential damage to the pipe structure.
By understanding the mechanisms and dynamics of the natural thawing process, homeowners and property managers can make informed decisions regarding thawing strategies and monitor the progress of thawing effectively. In the subsequent sections, we will explore the timeframe for natural thawing, methods for enhancing the thawing process, and important safety precautions to consider during the thawing journey.
Timeframe for Natural Thawing
Determining the timeframe for natural thawing is crucial for managing expectations and implementing effective strategies to address frozen pipes. While the exact duration can vary based on several factors, including the severity of freezing and ambient conditions, understanding the general timeframe can help homeowners and property managers make informed decisions. Here, we explore the key elements of the timeframe for natural thawing:
General Duration for Pipes to Thaw Naturally:
The time required for pipes to thaw naturally can vary widely depending on the extent of freezing and the characteristics of the pipes. In some cases, pipes may begin to thaw within a few hours, especially if the blockage is partial or the ambient temperature is relatively warm. However, complete thawing of heavily frozen pipes may take several days, requiring patience and diligence in monitoring progress.
Variables Affecting Thawing Time:
Several variables can influence the time required for pipes to thaw naturally. The thickness and material of the pipes, the severity of freezing, ambient temperature, and proximity to heat sources or insulation all play significant roles in determining thawing time. Thicker pipes and severe ice blockages generally require more time to thaw compared to thinner pipes or partial blockages.
Monitoring Techniques to Assess Progress:
Monitoring the progress of thawing is essential for assessing the effectiveness of thawing strategies and identifying any potential issues. Homeowners and property managers can use various techniques to monitor thawing progress, including observing changes in water flow, feeling for warmth along the pipe surface, and using temperature sensors or infrared thermometers to measure pipe temperatures.
By understanding the general duration for natural thawing and considering the variables that influence thawing time, homeowners and property managers can take proactive measures to address frozen pipes effectively. In the subsequent sections, we will explore methods for enhancing the thawing process, safety precautions, and preventative measures to mitigate the risk of future freezing incidents.

Enhancing Thawing Process
While natural thawing is effective, there are strategies to enhance the process and expedite the return of water flow within frozen pipes. By implementing these techniques, homeowners and property managers can minimize inconvenience and potential damage associated with frozen pipes. Here are key aspects of enhancing the thawing process:
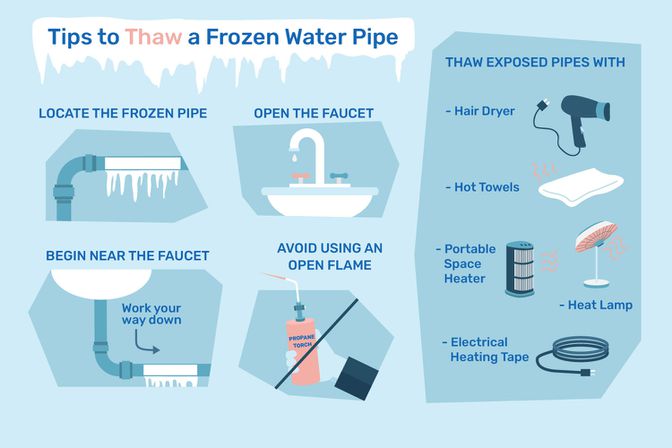
Application of Heat Sources:
Applying heat directly to frozen pipes is one of the most effective ways to expedite the thawing process. Heat sources such as space heaters, hairdryers, heat lamps, or electric heating pads can be strategically positioned near frozen sections of pipes to facilitate thawing. It’s essential to exercise caution and avoid using heat sources that pose a fire hazard or risk of overheating the pipes.
Opening Faucets to Relieve Pressure:
Opening faucets connected to frozen pipes can help relieve pressure within the plumbing system and encourage water flow. As the ice begins to thaw, water can gradually escape through the faucet, alleviating pressure and preventing potential damage from built-up pressure within the pipes.
Insulating Pipes to Prevent Refreezing:
Insulating pipes, especially those located in unheated or exposed areas, can help prevent refreezing and maintain thawed conditions. Pipe insulation sleeves or wraps, foam insulation, or heat tape can be applied to pipes to retain heat and minimize heat loss, reducing the risk of refreezing even in cold ambient temperatures.
By implementing these strategies in conjunction with natural thawing methods, homeowners and property managers can expedite the thawing process and restore water flow within frozen pipes more efficiently. In the subsequent sections, we will explore safety precautions to consider during the thawing process, as well as preventative measures to mitigate the risk of future freezing incidents and ensure the long-term integrity of the plumbing system.
Precautions and Safety Measures
While thawing frozen pipes, it’s crucial to prioritize safety to prevent accidents and minimize the risk of property damage. Implementing appropriate precautions and safety measures ensures a smooth and secure thawing process. Here are essential considerations to keep in mind:
Safety Guidelines When Applying Heat:
When using heat sources such as space heaters, hairdryers, or heat lamps to thaw frozen pipes, it’s essential to follow safety guidelines. Keep flammable materials away from heat sources, avoid placing heat sources near combustible materials, and never leave heat sources unattended. Additionally, use heat sources with built-in safety features and always follow manufacturer instructions.
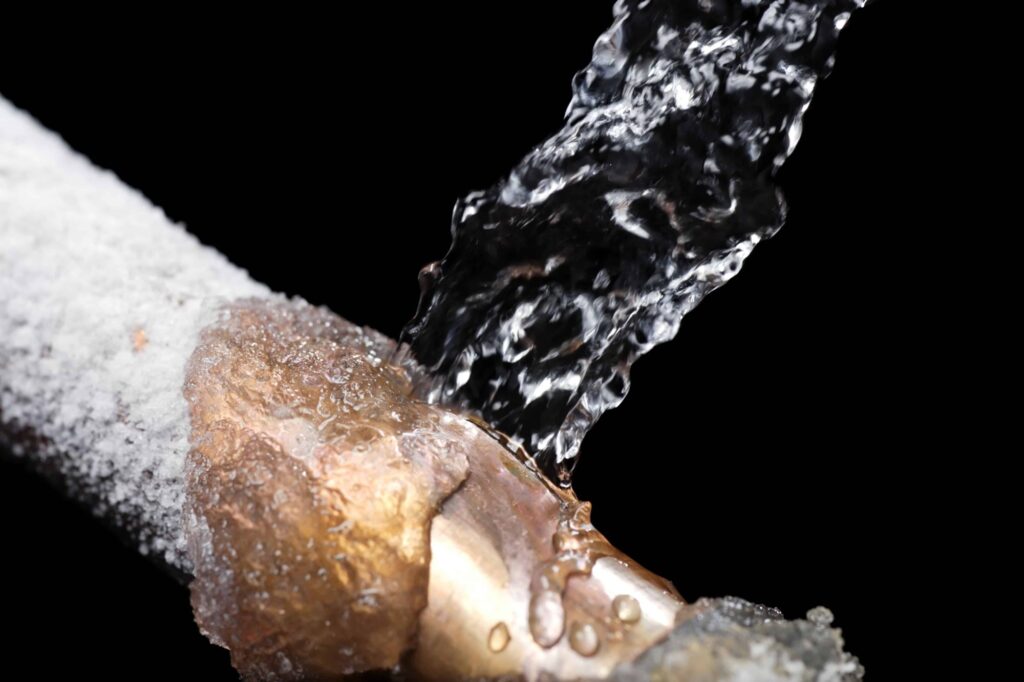
Monitoring for Signs of Burst Pipes:
During the thawing process, monitor the pipes closely for signs of burst pipes or leaks. Look for bulging or cracked sections of pipes, damp spots on walls or ceilings, or the sound of rushing water within walls or floors. If any signs of pipe damage are detected, immediately shut off the water supply and seek professional assistance to address the issue.
Seeking Professional Assistance When Necessary:
In some cases, thawing frozen pipes may require professional assistance, especially if the situation is complex or poses safety risks. If you encounter challenges during the thawing process or suspect significant damage to the plumbing system, don’t hesitate to contact a licensed plumber or professional plumbing service for expert guidance and assistance.
By adhering to these precautions and safety measures, homeowners and property managers can minimize the risk of accidents and ensure a safe and effective thawing process. In the subsequent sections, we will explore preventative measures to mitigate the risk of future freezing incidents and maintain the long-term integrity of the plumbing system.

Preventative Measures for Future Freezing
Preventing future freezing incidents is key to maintaining the integrity of the plumbing system and avoiding the inconvenience and potential damage associated with frozen pipes. Implementing preventative measures helps mitigate the risk of freezing and ensures the continued functionality of the plumbing infrastructure. Here are essential preventative measures to consider:
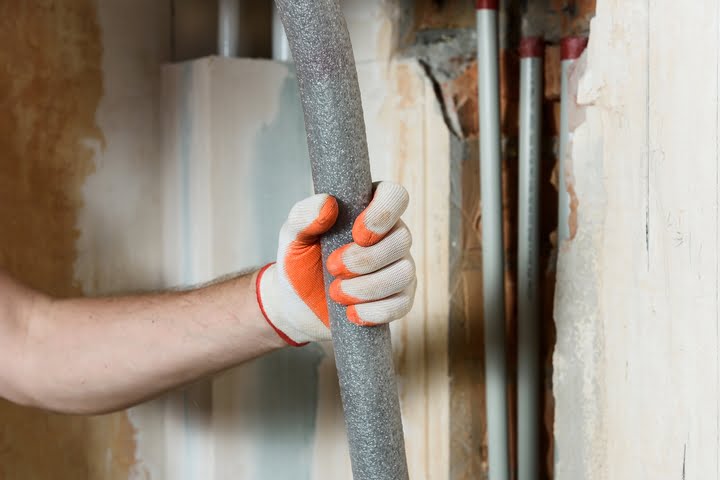
Insulating Pipes in Vulnerable Areas:
Identify and insulate pipes located in vulnerable areas, such as unheated crawl spaces, attics, or exterior walls. Pipe insulation sleeves, foam insulation, or heat tape can be applied to exposed pipes to retain heat and prevent freezing, even in cold ambient temperatures.

Allowing Faucets to Drip During Freezing Temperatures:
During periods of freezing temperatures, allow faucets connected to vulnerable pipes to drip slowly. The continuous flow of water helps prevent pipes from freezing by relieving pressure within the plumbing system and maintaining a consistent water flow. Even a slight drip can make a significant difference in preventing freezing.
Maintaining Consistent Indoor Temperatures:
Maintain consistent indoor temperatures throughout your home or property, especially in areas where pipes are located. Keep thermostats set to a minimum temperature, even when the property is unoccupied, to ensure that interior spaces remain warm enough to prevent freezing.
By implementing these preventative measures, homeowners and property managers can reduce the risk of future freezing incidents and maintain the functionality of the plumbing system year-round. In addition to these measures, regular inspection and maintenance of the plumbing infrastructure can help identify potential vulnerabilities and address them proactively, further minimizing the risk of frozen pipes and associated issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how long it takes for pipes to thaw naturally and implementing effective thawing strategies is crucial for homeowners and property managers facing frozen pipes. By comprehensively exploring the factors influencing thawing time, the natural thawing process, and methods for enhancing thawing efficiency, individuals can navigate the challenges of frozen pipes with confidence and resilience.
Throughout this guide, we have emphasized the importance of safety precautions and preventative measures to ensure a smooth and secure thawing process. By adhering to safety guidelines, monitoring for signs of pipe damage, and seeking professional assistance when necessary, individuals can minimize the risk of accidents and property damage during the thawing process.
Furthermore, implementing preventative measures such as insulating pipes, allowing faucets to drip during freezing temperatures, and maintaining consistent indoor temperatures can help mitigate the risk of future freezing incidents and ensure the long-term integrity of the plumbing system.
By combining knowledge, preparation, and proactive measures, homeowners and property managers can effectively address frozen pipes, prevent future incidents, and maintain the functionality of the plumbing infrastructure year-round. Remember, the key to successful thawing and prevention lies in understanding the dynamics of frozen pipes and taking appropriate action to safeguard against potential risks. With diligence and informed decision-making, individuals can navigate the challenges of frozen pipes with confidence and peace of mind.
