Contents
Introduction to Decreasing Testosterone Levels in Females
Testosterone, often associated with male characteristics, is also present in females, albeit in smaller amounts. While it plays a crucial role in female physiology, an imbalance in testosterone levels can lead to various health concerns and disrupt the delicate hormonal equilibrium. Maintaining balanced testosterone levels is essential for overall well-being and optimal functioning of the female body.
Understanding the complexities of testosterone regulation in females requires a nuanced exploration of its physiological significance and the factors influencing its levels. In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of decreasing testosterone levels in females, offering insights into the underlying mechanisms, potential consequences of imbalance, and strategies for achieving hormonal harmony.
Testosterone serves as a vital hormone in females, contributing to muscle strength, bone density, libido, and overall vitality. However, when testosterone levels exceed the normal range, it can lead to adverse effects such as hirsutism, acne, menstrual irregularities, and even infertility. The underlying causes of elevated testosterone levels in females are diverse, ranging from hormonal disorders like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) to adrenal gland abnormalities and certain medications.
In the pursuit of balancing testosterone levels, individuals can explore a myriad of lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, herbal remedies, and considerate monitoring under professional guidance. Dietary adjustments, exercise regimens, stress reduction techniques, and adequate rest form the cornerstone of lifestyle changes aimed at restoring hormonal balance. Meanwhile, medical interventions may include hormonal therapy, management of underlying conditions, and consultations with healthcare specialists to tailor treatment plans to individual needs.
Herbal and natural remedies offer additional avenues for hormone regulation, with phytoestrogen-rich foods, herbal supplements, and traditional remedies showcasing promising potential in supporting hormonal balance. However, it’s essential to weigh the benefits and risks of these approaches and seek informed advice from healthcare providers.
As we delve into the nuances of decreasing testosterone levels in females, it becomes evident that a holistic approach encompassing lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and thoughtful consideration of individual needs is paramount. By empowering individuals with knowledge, resources, and support, we aim to foster a journey towards hormonal harmony and enhanced well-being. Through informed decision-making, collaboration with healthcare professionals, and a commitment to holistic health, individuals can embark on a path towards balanced testosterone levels and vitality.
Understanding Factors Influencing Testosterone Levels
To comprehend the intricacies of decreasing testosterone levels in females, it is imperative to explore the factors that contribute to hormonal fluctuations and potential imbalances. Testosterone levels are influenced by a myriad of physiological and environmental factors, and a nuanced understanding of these elements is crucial for developing targeted strategies to restore hormonal equilibrium.
Normal Range of Testosterone Levels in Females:
Before delving into factors that may contribute to elevated testosterone levels, it is essential to establish a baseline understanding of the normal range of testosterone in females. While testosterone is present in smaller quantities in females compared to males, it plays a vital role in supporting various physiological functions, including muscle maintenance, bone density, and reproductive health. Understanding what constitutes a healthy testosterone level provides context for identifying and addressing imbalances.
Factors Contributing to Elevated Testosterone Levels:
Elevated testosterone levels in females can stem from a variety of sources, ranging from hormonal disorders to external influences. This section explores key contributors to increased testosterone levels:
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
PCOS is a common endocrine disorder characterized by enlarged ovaries with small cysts, often leading to hormonal imbalances. Elevated testosterone levels are a hallmark of PCOS, contributing to symptoms such as irregular menstrual cycles, acne, and hirsutism. Understanding the link between PCOS and testosterone elevation is crucial for effective management.
Adrenal Gland Disorders:
The adrenal glands, situated atop the kidneys, play a role in hormone production, including testosterone. Disorders affecting the adrenal glands, such as adrenal hyperplasia or tumors, can result in excessive testosterone production. Exploring the interplay between adrenal function and testosterone levels provides insights into potential sources of hormonal imbalance.
Medications and Hormonal Treatments:
Certain medications and hormonal treatments may inadvertently influence testosterone levels in females. For example, anabolic steroids or some forms of hormonal birth control can impact hormonal balance. Awareness of the potential effects of medications on testosterone levels is essential for informed decision-making and proactive management.
Consequences of High Testosterone Levels in Females:
While testosterone is vital for various physiological functions in females, an excess can lead to adverse consequences. Understanding the potential outcomes of high testosterone levels, such as acne, hirsutism, menstrual irregularities, and fertility issues, underscores the importance of addressing hormonal imbalances for overall well-being.
By exploring these factors contributing to elevated testosterone levels, individuals and healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into the root causes of hormonal imbalances. This understanding forms the basis for developing targeted interventions and personalized approaches to restore testosterone levels to a healthy range.
Lifestyle Changes to Decrease Testosterone Levels
In the journey towards restoring hormonal balance and decreasing testosterone levels in females, lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role. By adopting healthy habits and making mindful choices in diet, exercise, stress management, and sleep, individuals can exert significant influence over their hormonal milieu. This section delves into various lifestyle changes aimed at decreasing testosterone levels and promoting overall well-being.
Dietary Modifications:
Diet plays a crucial role in hormonal regulation, and specific dietary choices can impact testosterone levels in females. Embracing a diet rich in low-glycemic index foods, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help stabilize blood sugar levels and mitigate insulin resistance, a common factor contributing to elevated testosterone levels. Additionally, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods such as turmeric, ginger, and fatty fish can support hormonal balance and reduce inflammation throughout the body.
Exercise and Physical Activity:
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining hormonal balance and overall health. Engaging in cardiovascular exercises such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling helps promote circulation, reduce stress, and support metabolic health. Furthermore, incorporating strength training and resistance exercises can enhance muscle mass, improve insulin sensitivity, and aid in testosterone regulation. A balanced exercise regimen that includes both cardiovascular and strength training components is optimal for hormonal health.
Stress Reduction Techniques:
Chronic stress can contribute to hormonal imbalances, including elevated testosterone levels, by increasing cortisol production and disrupting the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. Implementing stress reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, and tai chi can help lower cortisol levels, promote relaxation, and restore hormonal equilibrium. Making time for self-care activities and prioritizing stress management is essential for supporting hormonal balance.
Adequate Sleep and Rest:
Quality sleep is paramount for hormonal regulation and overall well-being. Adequate rest allows the body to repair and regenerate, facilitating optimal hormone production and regulation. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing sleep environment can promote restorative sleep patterns. Additionally, prioritizing relaxation and downtime throughout the day helps reduce stress levels and support hormonal balance.
By integrating these lifestyle changes into daily routines, individuals can create a supportive environment for decreasing testosterone levels and restoring hormonal harmony. While the effects of lifestyle modifications may vary from person to person, consistency and commitment to healthy habits are key to long-term success in achieving hormonal balance and overall wellness.
Medical Interventions and Treatments
In cases where lifestyle modifications alone may not sufficiently decrease testosterone levels in females, medical interventions and treatments offer additional avenues for restoring hormonal balance. These interventions are often tailored to address underlying hormonal disorders, manage symptoms, and optimize overall health. This section explores various medical interventions and treatments commonly used to decrease testosterone levels in females.
Hormonal Therapy:
Hormonal therapy is a cornerstone of treatment for individuals with elevated testosterone levels, especially those with underlying hormonal disorders such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Oral contraceptives containing estrogen and progestin are commonly prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles, suppress androgen production, and alleviate symptoms associated with high testosterone levels. Anti-androgen medications, such as spironolactone, may also be used to block the effects of testosterone and reduce symptoms such as hirsutism and acne.
Management of Underlying Conditions:
Effective management of underlying hormonal disorders, such as PCOS or adrenal gland disorders, is essential for decreasing testosterone levels and restoring hormonal balance. Treatment modalities may vary depending on the specific condition and may include lifestyle modifications, hormonal therapy, and medications aimed at addressing symptoms and regulating hormone levels. Collaborative care involving endocrinologists, gynecologists, and other healthcare specialists is often necessary to develop comprehensive treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals:
Consulting with healthcare professionals is crucial for accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment planning, and ongoing monitoring of hormonal levels and symptoms. Endocrinologists, gynecologists, and women’s health specialists play key roles in evaluating hormonal imbalances, prescribing appropriate medications, and providing guidance on lifestyle modifications. Regular follow-up appointments allow for adjustments to treatment plans based on individual responses and evolving health needs.
While medical interventions and treatments can be effective in decreasing testosterone levels and managing symptoms, it is essential to weigh the potential benefits and risks associated with each option. Healthcare providers work collaboratively with patients to discuss treatment goals, address concerns, and develop individualized approaches that prioritize safety, efficacy, and overall well-being.
By embracing medical interventions in conjunction with lifestyle modifications, individuals can take proactive steps towards restoring hormonal balance, alleviating symptoms, and optimizing overall health and quality of life. Open communication with healthcare providers and adherence to treatment recommendations are essential components of a comprehensive approach to managing elevated testosterone levels in females.
Herbal and Natural Remedies
In addition to medical interventions and lifestyle modifications, herbal and natural remedies offer alternative approaches for decreasing testosterone levels in females and promoting hormonal balance. These remedies, often derived from plant-based sources, are valued for their potential to support hormone regulation without the side effects associated with pharmaceutical interventions. This section explores various herbal and natural remedies commonly used to address elevated testosterone levels in females.
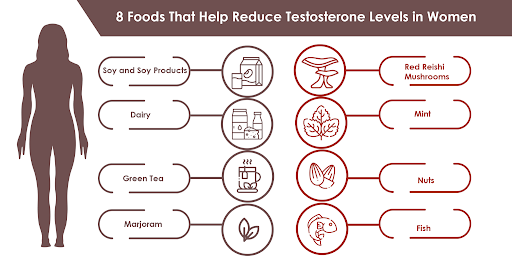
Phytoestrogen-Rich Foods and Supplements:
Phytoestrogens are plant-derived compounds that exhibit estrogen-like effects in the body and may help regulate hormonal balance. Foods rich in phytoestrogens include soy products, flaxseeds, chickpeas, lentils, and alfalfa sprouts. Incorporating these foods into the diet may help modulate estrogen and testosterone levels, potentially reducing symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances. Additionally, phytoestrogen supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, powders, and extracts, although their efficacy and safety require further research.
Herbal Remedies for Hormonal Balance:
A variety of herbs and botanicals are traditionally used to support hormonal balance and alleviate symptoms associated with elevated testosterone levels. Some commonly used herbs include:
Saw Palmetto: Saw palmetto extract is believed to inhibit the conversion of testosterone to its more potent form, dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It is often used to manage symptoms such as hirsutism and hair loss in females with elevated testosterone levels.
Spearmint: Spearmint tea is popularly consumed for its potential anti-androgenic effects, which may help reduce testosterone levels and alleviate symptoms of hirsutism and acne.
Black Cohosh: Black cohosh is traditionally used to alleviate symptoms associated with hormonal fluctuations, including hot flashes, mood swings, and menstrual irregularities. While research on its efficacy in decreasing testosterone levels is limited, some women may find relief from symptoms with regular use.
Potential Benefits and Risks of Herbal Treatments:
While herbal remedies offer promising potential for hormone regulation, it is essential to consider both their benefits and risks. While some herbs may effectively decrease testosterone levels and alleviate symptoms, others may have limited scientific evidence supporting their efficacy or carry potential risks of adverse effects or interactions with medications. Additionally, the quality and purity of herbal supplements can vary, making it essential to source products from reputable manufacturers and consult with healthcare professionals before use.
Incorporating herbal and natural remedies into a comprehensive treatment plan for elevated testosterone levels requires careful consideration and consultation with healthcare providers. While these remedies may offer alternative approaches to hormonal balance, they should be viewed as complementary to, rather than a substitute for, medical interventions and lifestyle modifications. By taking an informed and holistic approach to hormone regulation, individuals can explore a variety of options and tailor their treatment plans to meet their unique needs and preferences.
Considerations for Specific Population Groups
When addressing elevated testosterone levels in females, it is essential to recognize that individual experiences may vary based on factors such as age, reproductive status, and underlying health conditions. Specific population groups may have unique considerations and treatment needs that warrant careful attention and tailored approaches. This section explores key considerations for pre-menopausal women, post-menopausal women, and women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or hormonal imbalances.
Pre-Menopausal Women:
Pre-menopausal women experience fluctuations in hormone levels as part of their natural menstrual cycle. Elevated testosterone levels during this phase may be associated with conditions such as PCOS or adrenal gland disorders. Treatment approaches for pre-menopausal women may focus on regulating menstrual cycles, managing symptoms such as hirsutism and acne, and addressing underlying hormonal imbalances. Hormonal contraceptives, anti-androgen medications, and lifestyle modifications are commonly used interventions to restore hormonal balance in pre-menopausal women.
Post-Menopausal Women:
Post-menopausal women undergo hormonal changes as a result of declining estrogen levels and cessation of menstrual cycles. While testosterone levels may decline with age, some women may still experience symptoms of elevated testosterone levels due to underlying conditions such as PCOS or adrenal gland disorders. Treatment approaches for post-menopausal women may include hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to alleviate symptoms of hormonal imbalance and support overall well-being. Lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and stress management techniques are also important considerations for promoting hormonal health in post-menopausal women.
Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) or Hormonal Imbalances:
Women diagnosed with PCOS or other hormonal imbalances require specialized care to address their unique needs and symptoms. PCOS is characterized by elevated levels of androgens, including testosterone, leading to symptoms such as irregular menstrual cycles, hirsutism, acne, and infertility. Treatment strategies for women with PCOS may involve a combination of hormonal therapy, lifestyle modifications, and management of associated conditions such as insulin resistance and obesity. Close monitoring and regular follow-up with healthcare providers are essential for optimizing treatment outcomes and addressing long-term health concerns.
Tailoring treatment approaches to specific population groups requires a comprehensive understanding of individual health histories, symptoms, and treatment goals. Healthcare providers collaborate with patients to develop personalized treatment plans that address underlying hormonal imbalances, alleviate symptoms, and support overall well-being. By recognizing the unique considerations of each population group, individuals can access targeted interventions and resources to effectively manage elevated testosterone levels and optimize hormonal health throughout different stages of life.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Effective management of elevated testosterone levels in females requires ongoing monitoring and follow-up to assess treatment efficacy, track changes in hormonal levels, and address any emerging symptoms or concerns. Regular monitoring allows healthcare providers to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, make adjustments to treatment plans as needed, and provide support to individuals throughout their journey to hormonal balance. This section outlines key aspects of monitoring and follow-up for individuals managing elevated testosterone levels.
Regular Hormone Level Testing:
Regular hormone level testing is essential for monitoring changes in testosterone levels and assessing the effectiveness of treatment interventions. Blood tests, including total testosterone levels and free testosterone levels, provide valuable insight into hormonal balance and help guide treatment decisions. Frequency of hormone level testing may vary depending on individual circumstances and treatment protocols, with some individuals requiring more frequent monitoring than others.
Monitoring of Symptoms and Side Effects:
In addition to hormone level testing, monitoring of symptoms and side effects is integral to assessing treatment response and overall well-being. Individuals are encouraged to track changes in symptoms such as hirsutism, acne, menstrual irregularities, and mood disturbances, and communicate any concerns or new symptoms to their healthcare providers. Close attention to potential side effects of medications or interventions allows for timely intervention and adjustment of treatment plans to minimize discomfort and optimize outcomes.
Adjustments to Treatment Plans as Needed:
Treatment plans for elevated testosterone levels in females are dynamic and may require adjustments over time based on individual responses, changes in symptoms, and evolving health needs. Healthcare providers collaborate with individuals to review treatment progress, discuss any challenges or concerns, and explore alternative interventions as needed. Flexibility and open communication are essential for optimizing treatment outcomes and promoting long-term hormonal balance and well-being.
Individuals are encouraged to actively participate in the monitoring and follow-up process, engage in open communication with their healthcare providers, and advocate for their health needs and preferences. By fostering a collaborative relationship with healthcare providers, individuals can navigate the complexities of managing elevated testosterone levels with confidence and empowerment. Regular monitoring and follow-up provide opportunities for ongoing support, education, and adjustment of treatment strategies to promote optimal hormonal health and overall quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the management of elevated testosterone levels in females requires a comprehensive and multifaceted approach that integrates lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, herbal remedies, and tailored considerations for specific population groups. By addressing underlying hormonal imbalances, alleviating symptoms, and promoting overall well-being, individuals can achieve hormonal harmony and optimize their quality of life.
Throughout this exploration, we have highlighted the importance of understanding the factors influencing testosterone levels, including hormonal disorders, medications, and lifestyle factors. We have also discussed various strategies for decreasing testosterone levels, such as dietary modifications, exercise regimens, stress management techniques, and medical interventions tailored to individual needs.
It is crucial for individuals to work collaboratively with healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans that address their unique health circumstances and treatment goals. Regular monitoring and follow-up allow for adjustments to treatment strategies, evaluation of treatment efficacy, and support for individuals navigating the complexities of hormonal balance.
As individuals embark on their journey to manage elevated testosterone levels, it is essential to prioritize self-care, advocacy, and informed decision-making. By embracing holistic approaches to hormone regulation, individuals can cultivate resilience, empower themselves with knowledge, and foster a sense of agency over their health and well-being.
In closing, let us acknowledge the importance of ongoing education, support, and community engagement in promoting hormonal health and vitality. Through collaboration, compassion, and commitment to holistic wellness, individuals can navigate the challenges of managing elevated testosterone levels with grace, resilience, and empowerment. May this journey inspire individuals to embrace their unique health needs, advocate for their well-being, and embark on a path towards hormonal balance and thriving.